"Quality cannot be an accident. It is always the result intelligent effort." John Ruskin.
The software that powers technology today is what controls their behavior. Software Testing, also known as Quality Assurance, is essential because it identifies bugs and errors from a system right at the beginning. This article will give you detailed information about the various types of Software Testing.
- Introduction to Software Testing
- Software Testing is necessary.
- Software Testing Life Cycle
- Types of software testing
Introduction to Software Testing
Software testing is the process of evaluating a software program's functionality to identify any bugs. This process verifies that the software meets the requirements. It also identifies any defects in the software to ensure a high-quality product.
It can also be described as the verification and validation of a software product. It determines whether the software product is valid.
- It meets the technical and business requirements that influenced its design and development
- Work as required
- Can be used with the same characteristics
Let's continue with our article. We will now take a look at why software testing is important.
Software Testing is Important
Software testing is essential. This is a critical step that can have serious consequences for the product and the business. Let's take a look at the main points that will explain why you product needs to be tested.
Affordable
It is possible to save money by testing our projects on time. Software development is a series of stages. If bugs are caught early, it will be much cheaper to fix them.
Security
This is the most vulnerable and sensitive part of software testing. Trusted products are what users seek out. This helps to eliminate potential problems and reduce risks.
Product Quality
It is essential that your product vision comes to life. You can get the desired results by following the product requirements.
Customer Satisfaction
Product owners should strive to provide the highest level of customer satisfaction. To provide the best possible user experience, software should be tested.
These are just a few reasons why software testing is important. Let's continue with our article, and let us look at the various phases of the Software Testing Life Cycle.
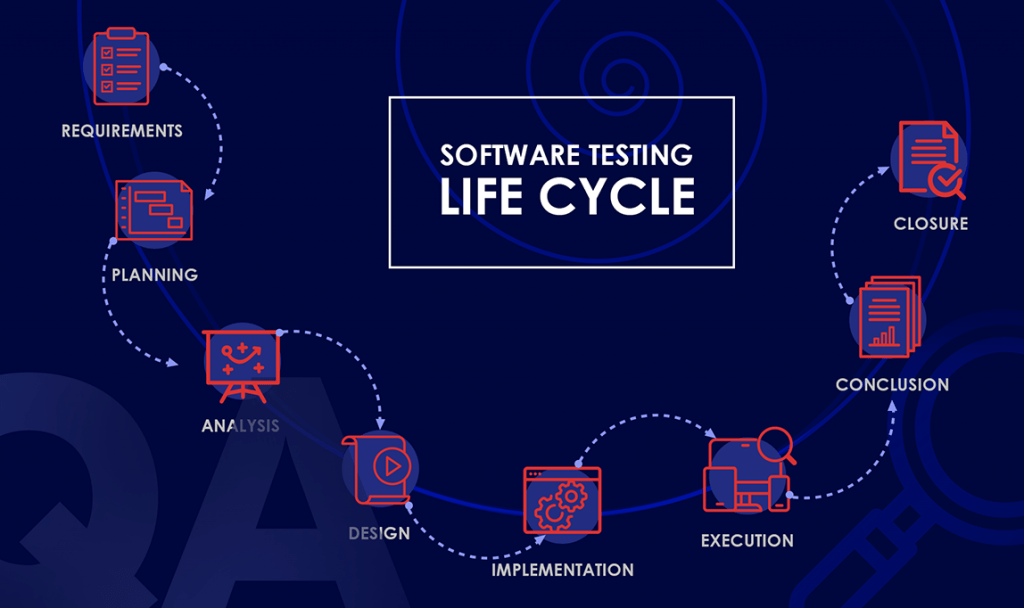
Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC).
Software Testing Lifecycle is a series of activities that the testing team performs to ensure quality software and products. It describes a set of activities that are used to perform Software Testing.
These are the phases of the Software Testing Life Cycle.
- Requirement analysis -- The first step in the Software testing lifecycle is Requirement analysis. This step is where Quality Assurance (QA), the team responsible for Software testing, understands the requirements in terms of what they will test and determines the testable requirements.
- Test planning -- This is where all the testing strategies are defined. This phase is also known as Test Strategy phase. This phase is where the Test Manager participates to estimate the cost and effort for the entire project. This phase defines the scope and objective of the project.
- Test Case Development -- After the test planning phase has been completed, the Test case development phase begins. This is where the testing team takes notes on the test cases. A testing team prepares test data and test cases. These test cases can be reviewed by peers or the QA lead once they are completed.
- Setup of a Test Environment -- The Software Testing Lifecycle is not complete without setting up a test environment. The testing environment is the setup of hardware and software for testing teams to run test cases. It allows test execution using hardware, software, and network configurations.
- Test Execution -- This is the next stage in the Software Testing Life Cycle. Execution is the execution of the code and the comparison of the actual and expected results. Test execution starts when the test analysts execute the test scripts according to the project's test strategy.
- Test Cycle Closure This is the final phase in the Software Testing Life Cycle. This involves calling out the testers and evaluating their cycle completion criteria on the basis of Test coverage, quality, cost, time, critical business objectives, and software.
Let's continue with our article to learn more about different types of testing.
Software Testing Types
Software projects that are successful include testing. Software testing can be done in many ways depending on the project requirements, budget, timeline and expertise. The tester is responsible for determining the best type of testing to be done on the applications. Software testers or QA can perform both functional and non-functional testing.
Functional Testing
Functional testing is a method of ensuring that the functionality of a software application works in accordance with the requirements specification. Functional testing includes both manual and automated testing.
There are many types of functional testing.
Unit Testing
This is software testing at the individual component/unit level. This is done to verify that the software works as intended. One unit is the smallest part that can be tested for any software. A unit usually contains one or more inputs, and usually only one output.
The Benefits of Unit Testing
- Unit testing improves confidence when changing or maintaining code. Good unit tests should be written and run each time code is modified.
- Codes can be reused more often. Modular codes are essential for unit testing.
- The development process is quicker. It takes less effort to find and fix bugs during unit testing than it does during system testing or acceptance tests.
- A defect discovered during unit testing costs less than those found at higher levels.
- Debugging is simple. Debugging is easy if a test fails.
Integration Testing
This is a type of software testing in which individual units are tested together and then tested as a whole. This level of testing is used to find faults in interactions between integrated units.
Methods of Integration Testing
- Big Bang Integration Testing is a method that allows all or most units to be combined and tested in one go. This is when the whole software is given to the testing team in a single package.
- Top down is a method of Integration Testing in which top-level units get tested first, and then lower-level units get tested step-by-step. This approach can be used when top-down development is followed.
- Bottom upis a method of Integration Testing in which lower-level units are first tested and then the upper-level units are tested step by step. This approach can be used when bottom-up development is followed.
- Sandwich/Hybrid Integration Testing is a hybrid of both Top Down and Bottom Up.
System
This is the highest level of software testing, where an integrated and complete software system is tested. This test is used to assess the system's compliance to the requirements.
Tasks Performed By System Testing
- System Test Plan
- Prepare
- Review
- Rework
- Baseline
2. System Test Cases
- Prepare
- Review
- Rework
- Baseline
3. System Test
Interface
There are many components to an application, software, or website that is created. These components could include server, database and other related parts. Interface is the connection that enables and integrates these components. It is used to verify that the communication between these systems has been done correctly.
3 Phases of Interface Testing
- Development - After the interface has been configured, it is necessary to verify that the configurations are correct.
- Validation -- After the development has been completed, it is necessary to validate and verify the interface. This can also be done in unit testing.
- Maintenance When we begin to develop an interface, it is important to ensure that there are no defects in the code. Therefore, tests must be run on the interface.
Regression Testing
Regression testing is an important stage in the product's development and very helpful for developers to determine the product's stability with changing requirements. Regression testing is used to ensure that any code changes in the software do not affect the functionality of the product.
Regression Testing Techniques
- All Retest the entire test suite -- To ensure there aren't any bugs caused by a code change, all test cases are re-executed.
- Regression Testing Selection -- This method selects test cases from the test suite that will be re-executed. The entire test suite may not be re-executed. The code changes in the module determine the test cases.
- Test Case Prioritization -- High Priority test cases are prioritized over those with medium or low priority. The priority of a test case is determined by its importance and impact on the product.
- Hybrid - The hybrid technique combines Regression test selection with Test Case Prioritization. We select the test cases that are re-executed based on their priority.
Acceptance Testing
Acceptance Testing is a type of software testing that tests a system for its acceptability. This test evaluates the system's compliance to business requirements and determines whether it can be delivered.
Types Of User Acceptance Testing
- Product Acceptance Testing (BAT) - This is used to determine if the Product meets business goals and objectives. This test focuses on the business benefits that are most important due to changing market conditions.
- Contract Acceptance testing (CAT) -- This contract specifies that the Product must go live within a specified period. The acceptance test must then be completed and should pass all acceptance use cases.
- Operational acceptance Testing (OAT), This is used to evaluate the Product's operational readiness and is non-functional. This includes testing for compatibility, maintenance, technical support availability, reliability and fail-over.
- Alpha Testing -- This is to evaluate the Product in the testing/development environment by a team of specialized testers, usually known as alpha testers.
- Beta testing -- This is used to evaluate the Product by exposing the product to real end-users (usually called beta testers/betas). The issues are addressed by continuous feedback from users.
We have now seen all the types of Functional Testing. Let's continue with the article to learn more about Non-Functional Testing.
Non-functional Testing
There are many software testing types that can be used to differentiate the work of the QA team while testing apps. This is used to test the system's performance to validate and verify its quality attributes.
These types of non-functional testing are:
Documentation Testing
Documentation testing allows you to estimate the testing effort required and test coverage. Software documentation can include test plans, test cases, requirements, and test plans.
Key areas for Testing Documentation
- Instructions If specific instructions are given for certain activities, it is likely that we will have test scenarios for those activities
- Examples --step by-step examples can be provided to help explain GUI screen inputs and syntax, clarify commands or other interfaces or show expected outputs or illustrate other important points.
- Messages When we encounter a problem, such as an error message or a warning message, it is important to verify that the message documentation is correct.
- Samples --samples can sometimes be used to document input files for tuning or initialization parameters.
Installation Testing
Installation testing is a form of quality assurance in the software industry. It focuses on the steps customers need to successfully install and set-up the new software. Testing may include full, partial, or uninstall/upgrade processes.
Installation Testing Tips
- Install the full version of the application
- Automated testing
- Installation of Required Disk Space Check-In
- Distributed Testing Environments
- Automate the checking of files after installation
- After installation, confirm that registry changes have been made
- Negative testing in Installation Testing
- Uninstallation testing
Performance
Performance testing is a method of software test that ensures software applications perform well within their expected workload.
Types Of Performance Testing
- Load testing is a method of performing performance testing to assess the system's behavior under increasing load.
- Stress testing is a method of performing performance testing to assess the behavior of a system when it exceeds its expected workload.
- Endurance testing is a form of performance testing that is used to assess the system's behavior when it is subject to a substantial workload.
- Spike testing is a method of performing performance testing to determine the system's behavior when it is subjected to a sudden and substantial increase in load.
Reliability Testing
Reliability testing ensures that the product works as intended. This is the exercise of an application to ensure that any failures can be detected before the system is deployed.
Reliability Testing
- Feature Test: Each function should be run at least once. The interaction between functions should also be minimized
- Regression testing: Any new functionality or removal of old functionalities in an application is subject to a regression test. This test ensures that no bugs are introduced.
- Load Test:Load tests are used to determine if the application can support the load without causing a break-down. To determine the break point of an application, load is gradually increased until it becomes hung, unusable, or breaks down.
- Reliability Testing Objectives:Restrictions such as software behavior under certain conditions, achievable objectives and time constraints can be applied before setting reliability testing objectives.
Security Testing
Security testing is a type of software testing that ensures that the system and its applications are secure. Security testing is designed to identify any weaknesses in the system that could lead to information being lost by employees.
Highlight Areas
- Network security: This refers to looking for weaknesses in the network infrastructure.
- System software security This involves assessing the weaknesses in the software that the application relies on.
- Client-side security for application security: This is about ensuring that the client can't be manipulated.
- Server-side Application Security: This refers to making sure that both the server code as well as its technologies are strong enough to resist any intrusion.
These are the types of Software Testing we use in our daily lives to ensure that software or applications do not fail.

Comments
Post a Comment